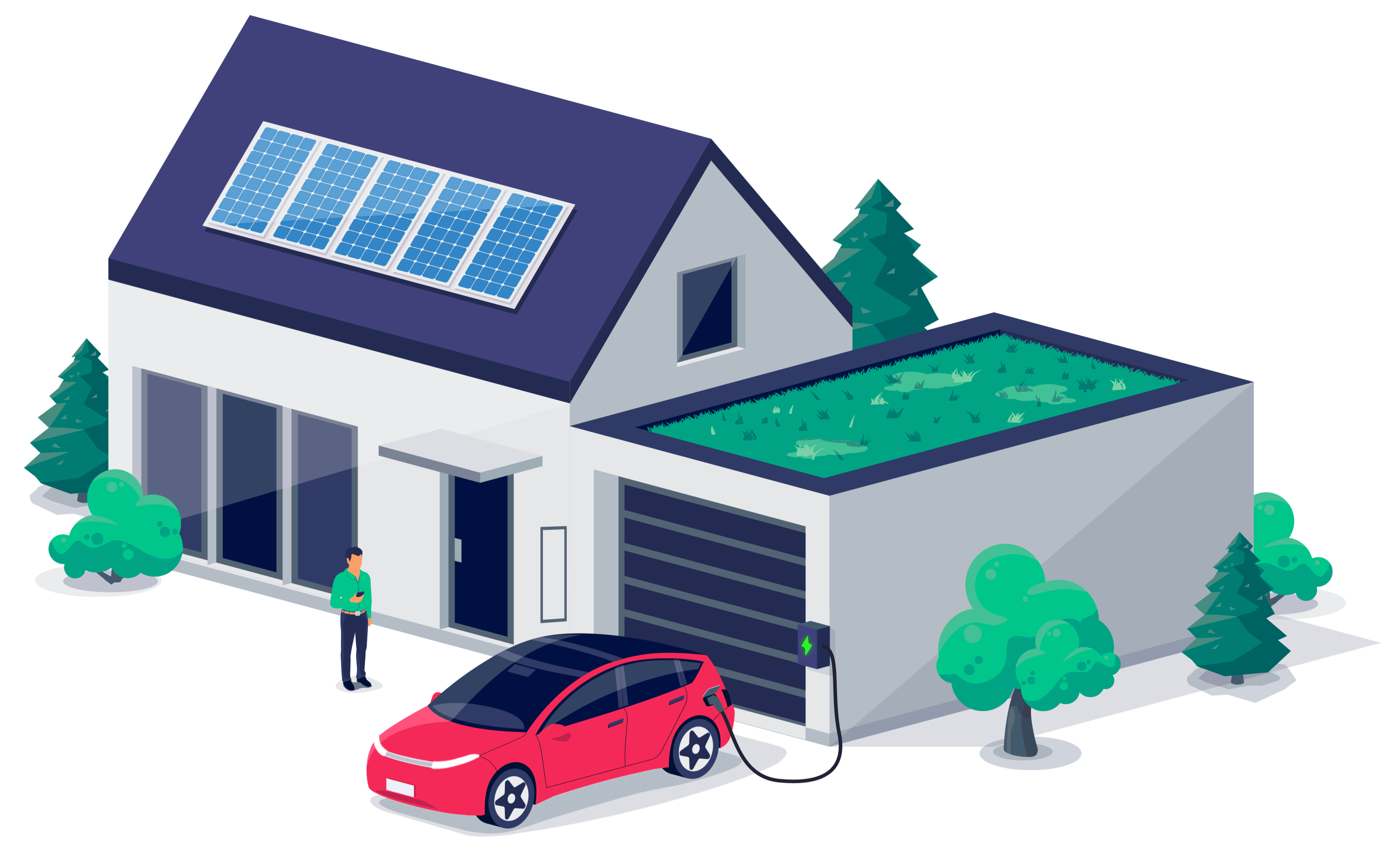
More and more people are starting to experience electric vehicles for the first time. Given that over 80% of EV charging happens at home, it’s time to forget the times of refueling at the gas pump. Electric vehicle charging is a totally new and different development, and it’s natural to have questions about how this EV charging works. To help you navigate through and be in control of your EV charging experience, here are the top 10 frequently asked questions about EV charging at home:
1. What are the Benefits of EV Charging At Home?
Driving an electric vehicle benefits the Earth, and charging that vehicle at home benefits YOU with:
- Convenience
- Control
- Cost Savings
- EV battery protection
- Increased home value
2. Where Can I Buy an at Home EV Charger?
When charging your EV at home you have two options - Level 1 and Level 2. Level 1 EV charging cords typically come standard with the purchase of the vehicle. If upgrading to Level 2, wall/pedestal mounted charging stations are often purchased directly online but can also be found in select hardware or electronics stores.
3. What are the Similarities and Differences Between Level 1 and Level 2 EV charging?
EV charging with either Level 1 or Level 2 involves feeding alternating current (AC) to the vehicle’s on-board charger which converts the AC power to direct current (DC) to charge the battery. Both chargers also use an SAE J1772 connector which is compatible with all non-Tesla electric vehicles in the United States (Tesla models come with an adaptor upon purchase). The key difference between Level 1 and Level 2 EV charging is charging rate. Level 1 EV charging cables use a standard 120V household outlet which only yields 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. On the other hand, Level 2 EV charging units require a 240V connection and yield 15 to 30 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers can also offer smart EV charging features.
4. Which Level of At-Home EV Charging is Best for me?
This is entirely dependent on your wants and needs. If you are an average commuter, traveling less than 40 miles per day, you can likely rely on Level 1. However, if you are a heavy commuter, traveling 40 to 100 miles per day, you will need to upgrade to Level 2. EV owners may also choose to upgrade to Level 2 if they already have the electrical capability installed, want to utilize smart EV charging features or want to be prepared in case of an emergency.
5. Why is a Level 3 Charging Station Not Ideal for Home Use?
Level 3 charging stations, typically found at public charging locations, present several challenges when considered for residential use.
First, the cost of installation is quite high, often running into several thousand dollars, making it an impractical option for most homeowners.
Second, these chargers require a tremendous amount of power—far more than a typical home electrical system can support. Installing one may require major electrical upgrades, which adds to the expense and complexity.
While Level 3 chargers offer extremely fast charging, their high cost and energy demands make them better suited for commercial or public use rather than home charging.
6. What Differentiates One At-Home EV Charging Station from Another?
Features that differentiate EV charging stations from one another include:
- Power
- Design (size, weight & aesthetic)
- Smart EV charging capability
- Mounting
- Cable length & management
- Wall plug
- Outdoor installation
- Certifications
- Warranty
7. What are the Benefits of a ‘Smart’ EV Charging Station?
Though not required, smart EV charging offers Level 2 EV owners the following benefits:
- Control EV charging from your smartphone - monitor, forecast, and schedule charging
- Informed decision making - access to data reports
- Cost savings - schedule charging for off-peak hours when energy rates are lower
- Bi-directional charging - transfer electricity flow from the EV battery to the home
- Utility incentives and rebates - only homeowners with networked chargers are eligible
8. How Much does EV Charging at Home Cost?
This is obviously dependent on where you live, what charger you have, and when you charge. One thing is certain - charging your EV is over 200% cheaper than filling up with gas. At the start of 2022, the average cost to add 100 miles of range was $14.08 with gas compared to $5.14 with electricity. EV charging at home is typically cheaper than public EV charging given the likelihood of charging during off-peak hours. However, installing a Level 2 charger at home will have upfront costs - typically $500 to $800 for charging hardware along with any electrical upgrades and installation costs.
9. How can the Cold Weather Affect Home Charging Stations for Electric Vehicles?
When temperatures drop, electric vehicle (EV) charging stations can face a few challenges. Understanding these impacts will help in managing your home charging setup effectively.
Factors Influencing Charging Efficiency in Cold Weather
- Slower Charging Times: Cold weather can significantly slow down charging times. This is mainly because batteries are less efficient at lower temperatures, requiring more power and time to reach a full charge.
- Battery Performance: Electric vehicle batteries tend to lose capacity in cold conditions. This means that an EV might need more frequent charges, potentially affecting the efficiency of your home charging station.
- Device Wear and Tear: Continuous exposure to freezing temperatures can lead to wear and tear on your charging equipment. Components like cords may become brittle and connectors can experience increased resistance, impacting the overall performance.
Ensuring Optimal Performance
- Install Indoors: Whenever possible, install your charging station in a garage or a sheltered area. This helps in maintaining moderate temperatures and protects equipment from harsh elements.
- Regular Maintenance: Conduct routine checks to ensure that all parts of your charging station are functioning well. Look for wear on cords and connectors, and replace anything that appears damaged.
- Preconditioning: Before plugging in, precondition your EV by warming it up to a moderate temperature. This process can help the battery accept a charge more efficiently.
By understanding these cold weather impacts and taking proactive measures, you can ensure that your home charging station continues to operate smoothly throughout the winter months.
10. What is the Best Time for EV Charging at Home?
The best time to charge an EV at home is during off-peak hours when energy rates are the cheapest. You can contact your energy provider to confirm, but off-peak hours are typically from midnight to morning. Utilize smart EV charging features or check your manual to determine how to schedule your charge.
11. How do I Install a Level 2 EV Charging Station?
If you have to ask - you shouldn’t! It is strongly recommended to consult a qualified electrician to help you select and install an EV charger. An electrician will be able to tell you if any electrical upgrades will be needed, where to install, if you are eligible for utility benefits, if approval is required, and more. If you are looking to strengthen your knowledge read National Electric Code (NEC) Article 625 which details EV charger installation requirements.
Charging your electric vehicle at home can be a seamless part of your daily routine. Whether opting for a simple plug-in or a more robust setup, understanding your options helps maximize the benefits of driving electric.
12. Are there any EV Charging Best Practices I Should Follow at Home?
Yes! One key tip for EV charging at home is to try to maintain your EV battery between 25% and 75%. Also, remember there are many factors that affect charging speed such as charging rate of the vehicle, battery size, battery fullness, and environmental elements such as temperature. Read our EV Charging Guide for a deep dive into EV charging best practices.
*BONUS QUESTION*: Can I charge my EV without power?
An EV should last a few days without needing a recharge. However, there is a way to overcome any extended power outage — solar and energy storage. Homeowners who install solar panels with an energy storage battery backup will be able to supply an EV, and their home, with power in case of an emergency. This can also save you money as energy can be saved when the rate is low and even sold back to the grid during peak demand.
Other articles in this Series on Electric Vehicles - New Trends in Technology.
----------------------------------------
Disclaimer:
The content provided is intended solely for general information purposes and is provided with the understanding that the authors and publishers are not herein engaged in rendering engineering or other professional advice or services. The practice of engineering is driven by site-specific circumstances unique to each project. Consequently, any use of this information should be done only in consultation with a qualified and licensed professional who can take into account all relevant factors and desired outcomes. The information was posted with reasonable care and attention. However, it is possible that some information is incomplete, incorrect, or inapplicable to particular circumstances or conditions. We do not accept liability for direct or indirect losses resulting from using, relying or acting upon information in this article.
ISO 9001:2015
Certified
17+ Million Product
Configurations
Lifetime
Warranty
Guaranteed
Same-Day Shipping
Advantage Pricing
Save Up To 40%
c3controls Headquarters, USA
664 State Avenue
Beaver, PA 15009